Advanced purification solutions for water, air, and industrial processes. Leveraging our industry expertise to deliver high-performance activated carbon products.
Activated carbon is a highly porous form of carbon with an exceptionally large surface area, making it an ideal material for adsorption applications. Through carefully controlled activation processes, ECORO develops activated carbon products with specific properties tailored to various purification requirements.
With decades of industry experience, our team at ECORO provides comprehensive expertise in activated carbon technologies, from material selection and activation methods to application-specific formulations and system integration. We offer both standard and customized solutions to meet the most demanding purification challenges.


Surface Area (m²/g)

Removal Efficiency

Years of Expertise

Custom Solutions Delivered
Understanding the science behind activated carbon's exceptional purification capabilities.

Raw organic materials are converted to carbon through controlled pyrolysis in an oxygen-limited environment, creating the basic carbon structure.

The carbonized material undergoes physical or chemical activation, creating millions of microscopic pores and dramatically increasing surface area.

Contaminant molecules are attracted to and bound to the activated carbon surface through various physical and chemical forces.
As water, air, or other media passes through activated carbon, contaminants are removed, resulting in purified output.
Explore our range of high-performance activated carbon solutions for various applications.

High-capacity granular activated carbon for water and air purification applications requiring excellent flow characteristics and minimal pressure drop.

Fine-grained activated carbon powder offering rapid adsorption kinetics and excellent performance for batch treatment processes and specialized applications.

Cylindrical pelletized activated carbon offering high mechanical strength and low dust generation, ideal for gas phase and vapor applications.
Activated carbon technologies provide effective solutions across a wide range of industries and applications.
Advanced water purification solutions for municipal, industrial, and point-of-use applications.
Effective removal of gaseous contaminants, odors, and volatile organic compounds from air streams
Specialized applications for industrial separation, purification, and recovery processes.
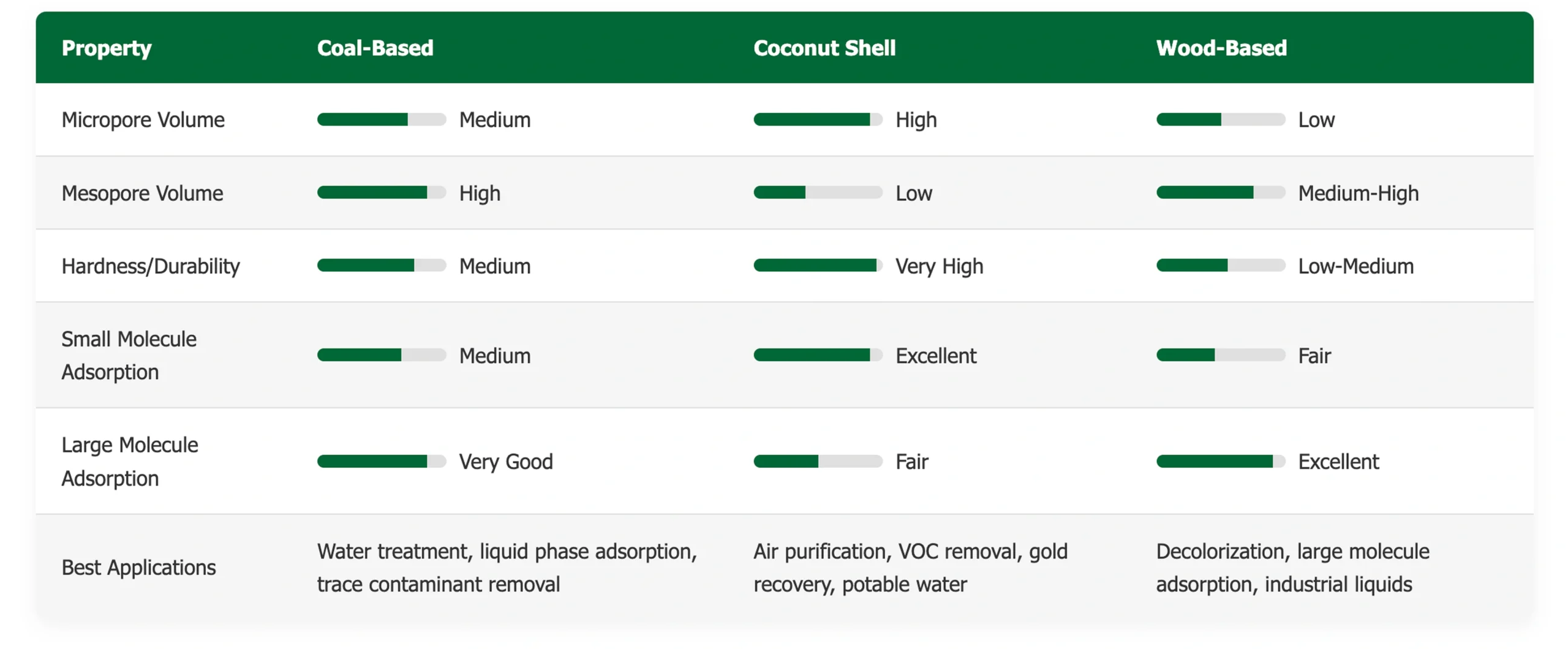
Understanding the performance characteristics of different activated carbon types to select the optimal solution for your application.

info@ecoro.nl



or get in touch with us at contact@ecoro.intl
Selecting the optimal activated carbon requires consideration of several factors including: the contaminants you need to remove, their concentration, the flow rate of your system, contact time available, operating conditions (pH, temperature, pressure), and regulatory requirements. ECORO's technical experts can help analyze your specific needs and recommend the most suitable product for your application.
Physical activation involves carbonizing raw materials and then activating the carbon using steam, carbon dioxide, or air at high temperatures (800-1000°C). This process creates micropores by selectively gasifying portions of the carbon structure. Chemical activation uses chemical agents like phosphoric acid, zinc chloride, or potassium hydroxide that are mixed with the raw material before carbonization. Chemical activation typically occurs at lower temperatures (400-700°C) and often results in higher yields and different pore size distributions. Each method produces activated carbon with different characteristics suited to specific applications.
The service life of activated carbon depends on various factors including: the type and concentration of contaminants, the volume of water or air being treated, the amount of carbon in use, operating conditions, and the specific application requirements. In general, activated carbon can last anywhere from a few months to several years. For water treatment applications, service life typically ranges from 6 months to 3 years, while air purification applications may range from 3 months to 2 years. Our technical team can help estimate expected service life for your specific application and develop an optimal replacement schedule.
Yes, in many cases spent activated carbon can be regenerated through thermal, chemical, or biological methods to restore its adsorption capacity. Thermal regeneration is the most common approach for industrial applications and involves heating the carbon to around 800-1000°C in a controlled environment to desorb and destroy contaminants. This process can typically recover 90-95% of the original activity. For some applications, onsite regeneration systems can be implemented, while in other cases, the spent carbon is sent to specialized facilities for regeneration. ECORO can provide guidance on regeneration options and sustainability considerations for your specific application.
Activated carbon is effective at removing a wide range of contaminants, particularly organic compounds. These include: chlorine and chloramines, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), pesticides and herbicides, industrial chemicals, disinfection byproducts, petroleum compounds, natural organic matter, taste and odor compounds, and some heavy metals when using specialized impregnated carbons. Activated carbon is less effective at removing inorganic compounds, very polar substances, and very small molecules like nitrates or fluoride. For comprehensive treatment, activated carbon is often used as part of a multi-barrier approach.
© 2025 ECORO BV. All Rights Reserved.